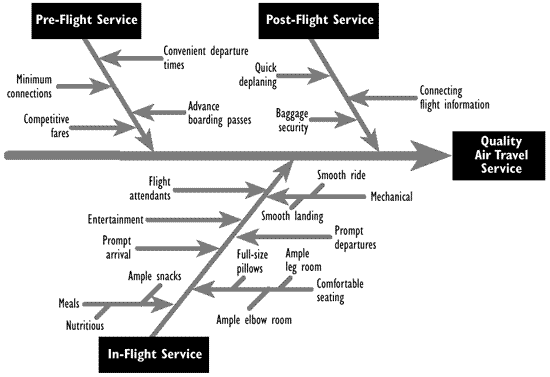
Figure 6C.1 - Example Ishikawa diagram
The Ishikawa diagram, also referred to as a cause-and-effect diagram, tree diagram, or fishbone diagram, displays the factors that affect a particular quality characteristic, outcome, or Problem. The diagram is named after its developer, Kaoru Ishikawa (1915-1989), a leader in Japanese quality control. An example is shown in Figure 6C.1.
An Ishikawa diagram is typically the result of a brainstorming session in which members of a group offer ideas on how to improve a product, process or service. The main goal is represented by the trunk of the diagram, and primary factors are represented as branches. Secondary factors are then added as stems, and so on. Creating the diagram stimulates discussion and often leads to increased understanding of a complex Problem. Japanese Circle members often post Ishikawa diagrams in a display area where they are accessible to managers and other groups. In the United States, Ishikawa diagrams are included in presentations by plant personnel to management or Customers.
Extracted from the SAS web site http.//www.sas.com/